Appendicitis
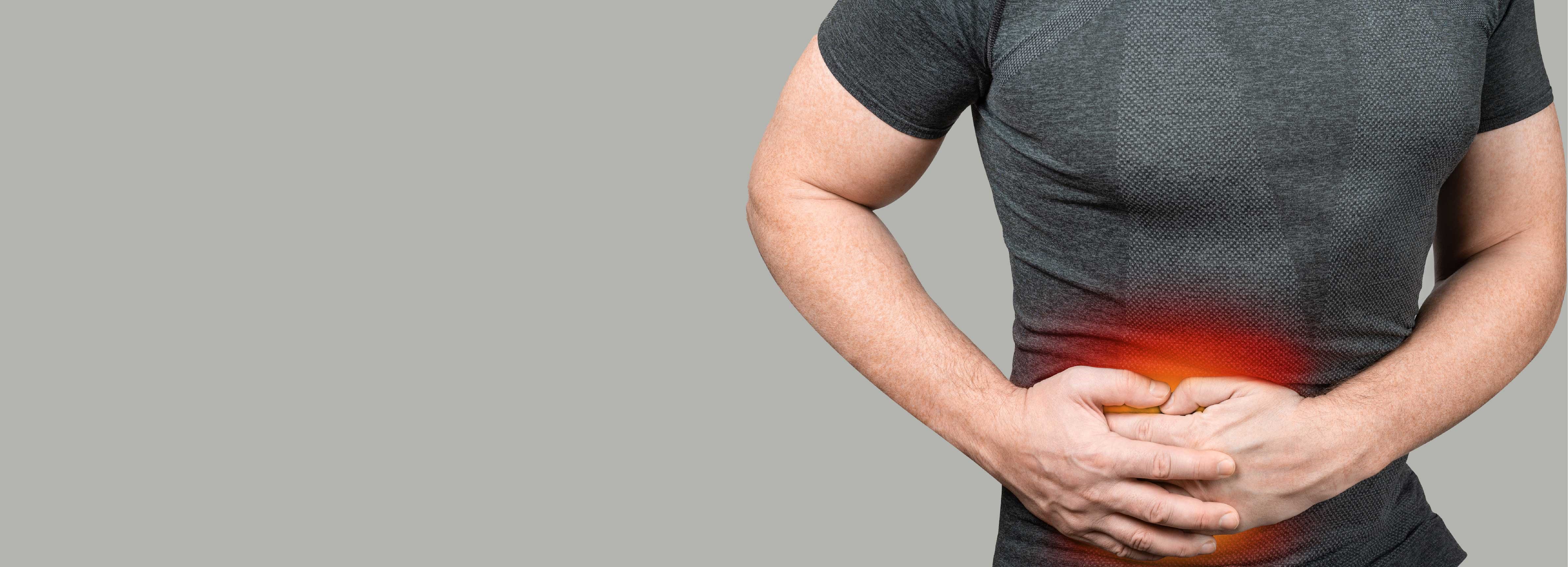
What Is Appendicitis?
Appendicitis is the inflammation of the appendix, a 6 to 9 cm long extension of the cecum located at the beginning of the large intestine. This inflammation can lead to the enlargement of the appendix, disrupt circulation, and potentially cause it to rupture.
The appendix is located in the lower right side of the abdomen. While its exact function is not clearly understood, recent studies suggest that the appendix may be related to the immune system.
Appendicitis usually occurs during adolescence but can also be seen in childhood and adulthood. Symptoms of appendicitis can sometimes be confused with those of gastroenteritis or a urinary tract infection. Diagnosing appendicitis in children can be particularly challenging, making prompt medical intervention necessary.
Causes of Appendicitis
The cause of appendicitis is related to the blockage of the lumen, a hollow section within the appendix. This blockage allows bacteria inside the appendix to multiply, leading to inflammation. As the severity of the inflammation increases, the symptoms of appendicitis become more noticeable.
Symptoms of Appendicitis
The most typical symptom of appendicitis is pain felt in the lower right part of the abdomen. The pain usually starts around the navel, spreads to the lower right side, and intensifies over time. Pain can increase with walking, coughing, or other movements. Nausea and vomiting are common accompanying symptoms. Patients with appendicitis often experience a loss of appetite. Some may also have dry mouth and tongue. Appendicitis can cause changes in bowel movements, leading to either constipation or diarrhea. There may be difficulty passing gas, straining during bowel movements, and pain. Increased heart rate and fever may occur in the later stages of appendicitis.
In pregnant women, appendicitis pain may also be felt in the side or back, and symptoms can sometimes be mistaken for pregnancy-related issues, making diagnosis challenging.
General symptoms of appendicitis include:
· Sudden and continuous pain in the lower right abdomen
· Fever
· Loss of appetite
· Nausea and vomiting
· Constipation or diarrhea
· Swelling in the inflamed area (abdomen)
Symptoms of Appendix Rupture
After an appendix rupture, the pain usually becomes more severe. There may be a significant increase in body temperature. Nausea and vomiting may become more frequent and continuous. Weakness, fatigue, and loss of energy can be felt. There may be a noticeable increase in heart rate. Blood may be present in stool and urine.
An appendix rupture is a serious condition and requires immediate medical attention if symptoms appear.
How Is Appendicitis Diagnosed?
To diagnose appendicitis, a doctor will perform a physical examination, and use methods such as blood tests, urine tests, and imaging tests (e.g., ultrasound or CT scan).
Appendicitis Surgery
Appendicitis surgery is typically performed using either laparoscopic surgery (minimally invasive) or open surgery (traditional). Laparoscopic surgeries generally require a shorter recovery period, allowing patients to be discharged more quickly, making it a preferred method.
Appendicitis surgery is usually performed under general anesthesia, meaning the patient is asleep during the procedure. During the surgery, small incisions (5-10 mm) are made in the abdomen, and a thin camera and special surgical instruments are inserted. The doctor views the area on a screen and removes the appendix. If the appendix has ruptured, the inflamed area is cleaned, and surrounding tissues are examined if necessary.
Laparoscopic surgery typically requires a short hospital stay, whereas open surgery may require a slightly longer stay.
In open surgery, a single large incision is made in the lower right abdomen. The surgeon accesses the abdominal cavity through this incision and removes the appendix.
After either type of surgery, the removed appendix may be sent for pathological examination.
Following the removal of the appendix, the patient typically recovers fully after a few weeks. However, after open surgery, strenuous physical activities should be avoided for up to 6 weeks.
Post-Appendicitis Surgery
Hospital stays after appendicitis surgeries are usually short. One of the advantages of laparoscopic surgery is a faster recovery period. Generally, most people who undergo laparoscopic appendectomy (minimally invasive surgery) are discharged within 24-48 hours, especially if there are no complications. Pain and discomfort in the first few days after surgery are normal. The doctor will recommend pain relievers and antibiotics.
Shoulder pain caused by gas may last for about a week after laparoscopic surgery. Constipation can occur post-surgery, so it is important to consume fiber-rich foods and drink plenty of fluids.
Patients typically start with water or liquid foods and gradually transition to solid foods. Following the doctor’s recommendations is crucial.
Care for the surgical site and guidelines on activities to avoid will be provided by the doctor before discharge. Generally, heavy lifting should be avoided for 4-6 weeks.
Appendicitis in Children
Appendicitis in children usually occurs between the ages of 5 and 15, although it can also appear at younger ages.
Symptoms of Appendicitis in Children
The symptoms of appendicitis in children can be similar to those in adults, but children may have difficulty expressing these symptoms.
The most notable symptom, abdominal pain, typically starts around the navel and then spreads to the lower right abdomen. A decrease in appetite and reluctance to eat may be observed. Appendicitis can cause nausea and vomiting, making the child feel uncomfortable. Fever is common with appendicitis, so it is important to regularly monitor the child's body temperature. The child may be sensitive to touch in the lower right abdomen. Appendicitis can also cause changes in bowel movements, so observing the child's bowel habits is important.
However, it is important to note that some cases of appendicitis occur without loss of appetite or fever, and blood tests may appear normal.
Appendicitis Surgery in Children
In recent years, selected cases have been treated with medication without the need for surgery. It is essential to understand that not all abdominal pain requires surgery.
However, if a child is diagnosed with appendicitis, the removal of the appendix may be necessary. When removal is required, the surgery is usually an emergency procedure and is performed within a few hours of hospital admission. Early diagnosis and surgery reduce the risk of appendicitis spreading and complications. Post-surgery, children are monitored in the hospital and, if there are no complications, can be discharged within 24 hours.
Post-Appendicitis Surgery in Children
Post-surgery, children may experience abdominal pain. The doctor will prescribe necessary pain relievers to manage the pain. The surgical incision or stitches should be regularly checked to prevent infection, following the doctor's recommendations is crucial. The child’s diet will typically start with liquids or light foods, and the doctor will guide you on when and what kind of foods to introduce. During the recovery period, children will gradually return to activities, but strenuous activities should be avoided for the first few weeks.
