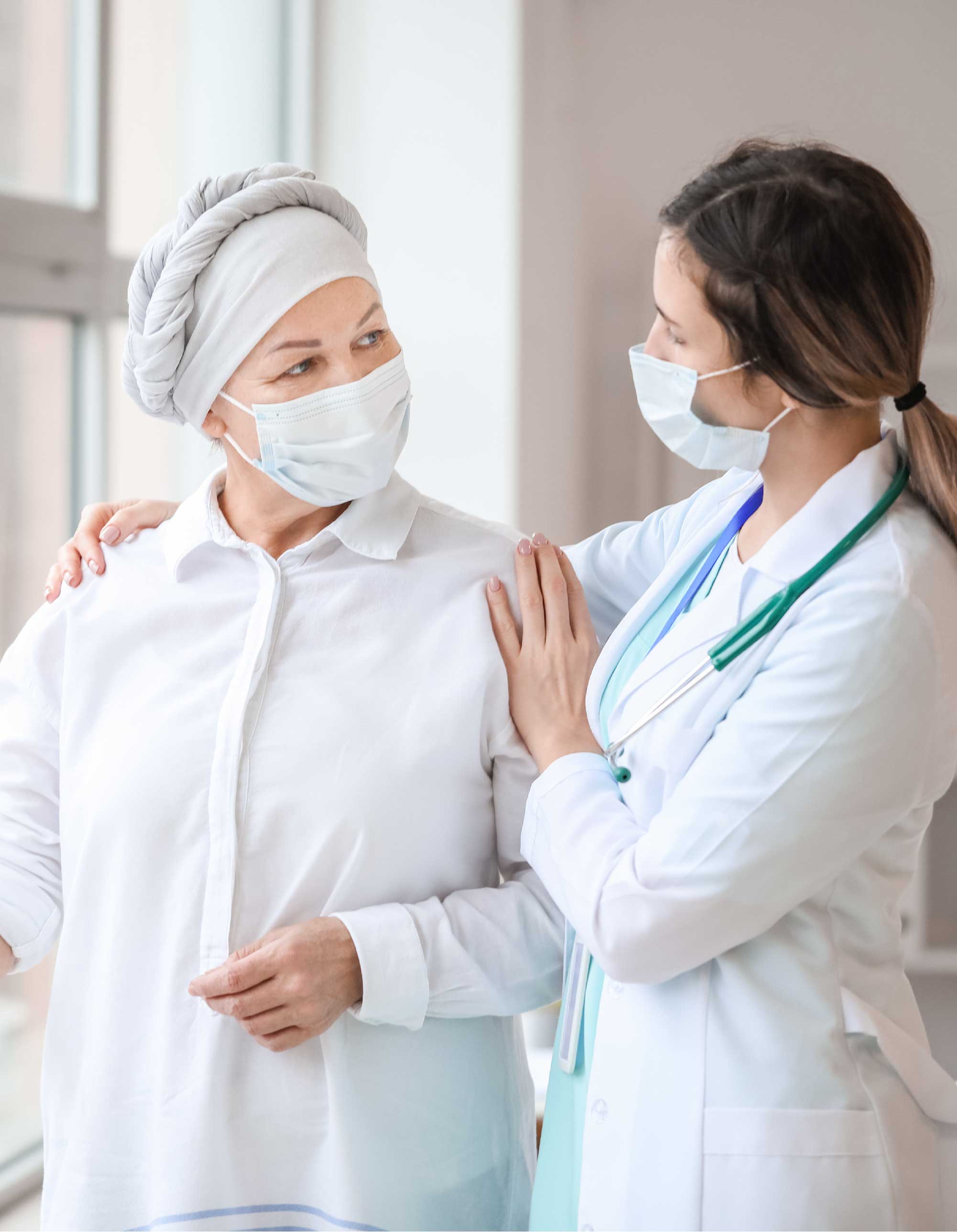
ONCOLOGY CENTER
All treatment approaches including medical treatment, radiotherapy, interventional, surgery and nuclear medicine approaches are carried out at our center. This allows us to prepare a customized treatment plan in a patient specific manner.

Cases are evaluated in the Multidisciplinary Tumor Council and Radiology, Nuclear Medicine, Genetic Testing, Pathological Testing and clinical evaluation are used to carry out a comprehensive diagnostic panel. This lets us confirm or establish diagnosis and plan the right treatment for our patients.

Guest House Accommodation integrated with the hospital allows for long or short-term stays needed for extended diagnostics or long-term treatment. The presence of dedicated accommodation right next door creates a comfortable and practical experience for our international patients.

All treatment approaches including medical treatment, radiotherapy, interventional, surgery and nuclear medicine approaches are carried out at our center. This allows us to prepare a customized treatment plan in a patient specific manner.
Radiology
Radiology plays a critical role in the diagnostic and evaluation stages of oncology patients. Our Center is equipped with the latest radiological imaging modalities such as 1.5 Tesla and 3 Tesla Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI), Computed Tomography (CT), and Nuclear Medicine Imaging technology. Apart from the high quality technological devices and negligible waiting times, highly trained Radiology Specialists and Technical Assisting staff ensure reliable results.
Our Hospital possesses the most advanced state-of-the-art radiology devices and all the diagnostic and interventional radiological procedures are carried out.The Department of Radiology has experienced physician team and the technical equipment that can meet all diagnostic and therapeutic needs of both patients and doctors. Our personnel show ultimate attention during the procedures to ensure that the patients are comfortable.Radiologists have the knowledge and experience to perform not only diagnostic procedures such as general radiology, computed tomography, mammography, panoramic x-ray, digital fluoroscopy, magnetic resonance imaging, ultrasound, color Doppler ultrasound and angiography but also therapeutic interventional procedures. The department renders services 24/7 for patients and reports are quickly transferred to doctors to accelerate diagnosis and treatment.
ULTRASOUND (US) AND DOPPLER ULTRASOUND
All ultrasonographic studies are performed such as abdominal, pelvic, renal, thyroid, thoracic, breast, hip, eye and cranial ultrasounds. Moreover, services include transrectal ultrasound, transvaginal ultrasound and intraoperative ultrasound. In addition to these studies, ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration and biopsies, fluid aspirations and catheter drainage procedures are performed.
Vascular structures and blood flow can be evaluated in detail with color Doppler ultrasound. Color Doppler ultrasound of arterial and venous system of upper and lower limbs, portal Doppler, Doppler ultrasound of carotid and vertebral arteries, orbital and scrotal Doppler, gynaecologic and obstetric Doppler, renal arterial Doppler and graft evaluation are also performed. These examinations are carried out by physicians who are highly experienced in this field. Unconditional patient satisfaction is one of the basic principles in the department; patients can schedule an appointment on the same day and waiting period for appointments is kept as short as possible.
All double contrast and biphasic examinations of gastrointestinal system are made and enterocylisis is performed to image the small intestine. Excretory urography, cystography, voiding cystourethrography and retrograde urography are amongst the genitourinary system studies. All hysterosalpingographies are performed under guidance of a gynaecologist and images are interpreted by radiologists. For fluoroscopic imaging, attention is paid to maximize quality of imaging, while minimizing the dose of radiation.
MAMMOGRAPHY
Mammography is a special examination performed with x-rays to diagnose breast cancer and other benign diseases of breast. Mammography services include screening tests for asymptomatic patients, diagnostic examinations for women with symptomatic breast diseases and stereotactic preoperative breast marking and consultations.
Technological specifications of the devices ensure optimal magnification and compression techniques with minimum radiation dose. The department provides accurate and fast diagnostic services for screening and diagnostic mammograms and galactography, ultrasound-guided breast marking and fine needle aspiration and biopsies are also performed successfully.
All images acquired by these devices are transmitted to PACS (Picture Archiving Communication Systems) and evaluated and stored by radiologists. As the system is integrated to the hospital information system (HIS), the results can be quickly reached by all outpatient and inpatient clinics and consultations can be made.
COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY (CT)
CT can form detailed and cross-sectional image of any body part and can be used for diagnosis of many diseases, ranging from soft tissue diseases to fractures. It is frequently used in conditions where other imaging methods, such as direct x-ray and ultrasound, cannot provide certain results. Spiral or sequential scanning is performed for any body part, such as brain, vertebra, thorax, abdomen and osseous and pelvic structures. Moreover, CT-guided biopsy and interventional procedures can also be carried out to reduce the need of surgery and for histopathological diagnosis of lesions.
MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING (MRI)
All neurologic examinations (brain, neck and vertebral column), vascular angiography (peripheral, intracranial, carotid and aorta), abdominal, thoracic and cardiac examinations, breast MRI, musculoskeletal system examinations, MRI cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), fetal MRI and functional MRI can be scanned. Functional MRI techniques include blood oxygenation level dependent (BOLD) imaging, diffusion and perfusion MRI, MRI spectroscopy and cerebrospinal fluid flow analysis. For the patients for whom definite diagnosis cannot be established with mammography and ultrasound, breast MRI can be canned to diagnose the breast cancer. MRCP ensures that bile ducts and pancreatic canals are non-invasively imaged and rapidly become a substitute for diagnostic ERCP studies. Radiology studies that require anesthesia administration can be performed under supervision of anaesthesiologist for patients in every age group in the department.

Hüdaverdi KARADEMİR
M.D.

Prof.
Ahmet Kemal FIRAT
M.D.

Fatma Hülya CENGİZ
M.D.

İshak İKİZ
M.D.

Asuman YİĞİT
M.D.

Oncologic Surgery
Apart from medical and radiotherapy approaches, our cancer center is equipped with experienced surgeons from all necessary branches to offer patients with surgical options during the course of cancer treatment. Oncoplastic surgery, Tumor Excision, Oncogynecologic, Urology, Head and Neck, Neurosurgery, Pediatric Surgery and General Surgery departments all participate in the Tumor Council to evaluate cases for the possibility of surgical intervention when necessary. Our center is suitable for complex or complicated cases requiring a multi-disciplinary approach consisting of a mix of multiple treatment modalities.
Pediatric Oncology
The Pediatric Oncology Department led by Prof. Dr. Birol Baytan is experienced in the entire range of Pediatric Oncology cases. As is the case in Adult Oncology, early diagnosis and treatment play a critical role in effective treatment results. The Pediatric Oncology Department treats patient in a separate department which is exclusive to pediatric patients and designed specifically with the needs of our young patients in mind.
Pediatric Hematology and Oncology Clinic Hematology is a branch of science dealing with blood and structure of bone marrow and their duties in body.Numerous blood diseases are diagnosed and treated in Pediatric Hematology-Oncology clinic, including but not limited to nutritional anemias (Iron Deficiency Anemia, Vitamin B12 Deficiency Anemia), Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia, Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Aplastic Anemia, Thalassemia (Mediterranean Anemia), Hemophilia.After examinations of pediatic patients are performed at our clinic, treatment methods to be performed are planned. Pediatric Hematology and Oncology Clinic has been designed as a special area with cutting-edge technology and medications can be prepared for child patients in sterile conditions by chemotherapy nurses.The area has been specifically designed in Emsey Hospital for needs of children and to boost their life quality within the period of time in which they stay at hospital. Primary Diseases Diagnosed and Treated at Pediatric Hematology and Oncology Clinic of Emsey HospitalRed blood cells and disorders related to them:Red blood cells include haemoglobin proteins that give the red colour to the blood. Red blood cells carry oxygen and carbon dioxide between tissues. They carry the carbon dioxide in tissues to lungs while they transmit the oxygen to the tissues from lungs.Therefore, in disorders of those cells:Anemia occurs with reducing in red blood cell count, fatigue, tiredness, poor exercise capacity, paleness, palpitation, decrease in success at school, memory impairment, bad temper, short posture, growth and developmental retardation may occur as nutrients and oxygen cannot sufficiently reach the organs. The most frequent causes of anemia: Iron deficiency, vitamin B12 deficiency, folic acid deficiency, zinc deficiency.Moreover, as a result of abnormal destruction of red blood cells: Diseases such as haemolytic anemia, G6PD deficiency, hereditary spherocytosis, autoimmune haemolytic anemia can develop.Diseases such as thalassemia (Mediterranean Anemia) sickle cell disease, fanconi aplastic anemia, aplastic anemia (bone marrow dysfunction) or polycytemia are also included in subjects of hematology.Disorders related to white blood cells:White blood cells are main self-defence weapons of our body. There are many types. Each cell has a different duty. They both produce the self-defence weapons that we call antibodies and they embody and digest the microbes on their own. In functional or quantitative disorders of white blood cells: Symptoms such as frequent health disorders, frequent fever, recurrent infections, aphta in mouth, recurrent otitis media-pneumonia-diarrhea, inability to gain weight and weight loss, skin inflammation can be observed.Moreover, abnormal amount of white blood cells (leukocytosis) should also be examined carefully. Disorders related to platelets and bleeding:Platelets are the smallest fragmented cells of blood. Vascular system hinders bleeding in cooperation with platelets and coagulation factors.In case of any disorder in these systems: Nasal bleeding, umbilical hemorrhage, bruising on body, long-lasting menstrual bleeding, deterioration in preoperative bleeding examinations, long-lasting bleeding following surgery and circumcision, gastric and intestinal bleeding, bleeding from urinary tracts, intraarticular bleeding and similar conditions occur.Diseases related to coagulation:Vascular occlusion in any part of body (thrombosis), stroke, occlusion in pulmonary vessels (pulmonary embolism), occlusion in renal veins (renal vein thrombosis), diseases like thrombophlebitis and hereditary conditions causing tendency to coagulation are included in the subjects of hematology.Pediatric CancersCancer means a group of diseases characterized with uncontrolled, invasive, abnormal cell division. The most common cancer types in pediatric age group are leukemia, central nervous system tumors, lymphoma. Moreover, many cancer types can be seen amongst children, although more rarely.Hearing and accepting the diagnosis of cancer is very difficult for families and children. However, remember that you are not along in this challenging path and cancer is now less frightening thanks to advancements in both diagnostic and therapeutic methods. Early diagnosis of cancer can increase success rates.In which conditions we should most frequently suspect cancer? One or more signs and symptoms can be noted depending on type, onset and spread regions of the diseases.For instance, frequently seen symptoms in cancers involving bone marrow such as leukemia are;
- Pallor, fatigue,
- Frequent fever, Bone pain,
- Bruising in skin,
- Swellings that are generally painless in lymph nodes,
- Swelling in any part of body,
- Nasal, gingival bleedings, blood in urine and stool without underlying reasons.
- Headache and vomiting severer in the mornings,
- Visual impairments,
- Gait disorders, imbalance,
- Strabismus, non-febrile convulsion, personality changes can be seen.

Assoc. Prof.
Doğan KÖSE
M.D.

Prof.
Birol BAYTAN
M.D.
General Surgery
Thanks to the depth of staff with different areas of interest, pioneering applications are carried out in gastrointestinal system (digestive system) surgery and hepato-pancreaticobiliary (liver, pancreas and biliary tract) surgery, especially in minimally invasive surgery, emergency surgery and endocrine (breast, goitre gland and adrenal gland) surgery. All interventions in colon and rectum (large intestine) diseases are performed using the most up-to-date technologies. In particular, a wide range of treatments are offered to our people in anal (rectal) region disorders such as haemorrhoids (haemorrhoids), fistulas or fissures (cracks).The disease grouping that can be examined, investigated and treated by the General Surgery Department is as follows:
• Thyroid Gland Diseases (Goitre, Hyperthyroidism)
• Breast Cancer and Benign Diseases of the Breast
• Oesophageal Cancer and Benign Diseases
• Anorectal Diseases: Tumours, Haemorrhoids, Anal Fissure, Anal Fistula
• Gallbladder and Duct Stones and Tumours
• Abdominal Wall and Inguinal Hernias, Postoperative Hernias
• Trauma and Emergency Surgery
• Stomach Cancer
• Hemorrhoids, Anal Fissure, Anal Fistula and Ingrown Hair Surgeries with Laser
• Surgical Diseases of the Small Intestine, Intestinal Obstructions
• Colon - Rectum Tumours, Inflammatory Diseases
• Benign and Malignant Tumours and Cysts of the Liver
• Obstructive Jaundice
• Pancreatic Cysts and Tumours
• Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis
• Surgical Diseases of the Spleen
• Various Soft Tissue Infections
• Laparoscopic Surgeries
• Obesity
• Diabetes Surgery
Laparoscopy is the observation of the abdomen using an optical device. This device is inserted into the abdomen through a small 1 cm incision below the navel. By illuminating the inside of the abdomen, it allows direct observation of diseases or problems involving the uterus, ovaries and tubes and, if necessary, simultaneous treatment with auxiliary instruments inserted through 3 - 5 mm holes in the lower abdomen. In laparoscopic surgery, operations are performed by means of a micro-camera inserted through several small holes in the abdominal wall, which is viewed on a screen.The Most Important Advantages of Laparoscopic Surgeries are as follows:
• There is very little bleeding during the operation.
• A very small scar remains.
• There is very little pain after the operation.
• Since there are no large incisions, the infection rate is lower.
• Since recovery is quicker, loss of work capacity is minimised.
• Hospital stay is short (maximum 1 day).
• It prevents intestinal adhesion due to surgery in the long term.

Prof. Dr.
Umut BARBAROS

Merih YILMAZ
M.D.
Hematology
- Anemia (Red blood cell deficiency, anemia)
- Leukopenia (White blood cell deficiency)
- Thrombocytopenia (Platelet deficiency)
- Polycythemia (Red blood cell excess, erythrocytosis)
- Leukocytosis (White blood cell excess)
- Thrombocytosis (Excess platelet)
- Sickle cell anemia: Anemia caused by a structural defect caused by a genetic mutation in hemoglobin molecules in red blood cells.
- Aplastic anemia: It is a rare, serious type of bone marrow failure that occurs when the bone marrow cannot make enough new blood cells.
- Autoimmune hemolytic anemia: It is a type of anemia that occurs when red blood cells are destroyed by the body's own immune system.
- Leukemia
- Lymphoma
- Multiple Myeloma
- Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS)
2- Hematological diseases originating from platelets
- Hemophilia
3- Platelet function disorders
- Von Willebrand's disease
- Primary thrombocytosis
- Simple blood count
- Microscopic examination of blood
- Molecular biological tests
- Flow cytometry
What is Bone Marrow Transplantation?
- The “stem cells” found in the bone marrow are responsible for the production of blood cells in the body. In cases where the bone marrow is damaged or lost its function, the reintroduction of new “stem cells” obtained through various means into the body through the vein is called “bone marrow transplant”.
- The person from whom the stem cells are taken is called a donor/donor, and bone marrow transplants are classified according to the donor. Namely;
- Autologous transplant:
- The donor is the patient himself. Stem cells taken from the patient are frozen and transplanted back to him after certain procedures. The aim here is to reset the bone marrow damaged by high-dose chemotherapy and/or radiotherapy to be given for treatment. Multiple myeloma, Hodgkin lymphoma, non-Hodgkin lymphoma and acute myeloid leukemia are among the diseases that autologous transplantation can be performed.

Prof.
Serdar Bedii OMAY
M.D.

Nuclear Medicine
The Nuclear Medicine Department is involved in both diagnostic and treatment stages of cancer treatment. PET – CT scanning, Gallium 68 PSMA scans, Scintigraphy procedures and Iodine scans are some of the cutting-edge diagnostics performed at our clinic. With the help of these advanced diagnostic modalities, our teams are able to perform high – quality staging and grading of cancer patients. Early diagnosis is one of the corner stones of effective cancer therapy and our clinic offers negligible waiting times for these screening and diagnostic procedures. Furthermore, the Nuclear Medicine Department also offers advanced treatment modalities including Actinium, Technetium, Samarium and Radioactive Iodine treatment options.
TREATMENT OF LIVER CANCER WITH MICRO-SPHERE METHOD
Liver cancer is a prevalent type of cancer not only in our country but also in U.S. and European countries. Successful outcomes are obtained in management of liver cancer with microsphere – a new generation therapy – along with chemotherapy and medication therapies. It took attention of medicine community due to almost total absence of side effect and other advantageous features.What are characteristics of liver cancer?Liver cancers are addressed in 2 main groups. First group involves primary cancers that imply cancerous formations originating from hepatic cells, while second group is metastatic tumors that metastasize from cancers of other organs. Primary liver cancers also imply hepatocellular cancers that originate from native cells of liver.What is difference of micro-sphere methods in comparison to other methods?Micro-sphere method is a specific therapy. Chemotherapy and medications are systemic therapy methods. In other words, they do not absolutely target the lesion in liver. “Specific therapy” implies that there will be no systemic side effect, or in other words, patient will not encounter exhaustive side effects that occur after chemotherapy.What is incidence of liver cancer?Five hundred thousand to 1 million new primary cancer cases are diagnosed per annum worldwide. When metastatic cases are considered, pancreas and colon cancers are most common ones.Hepatic metastases account for 50 to 70 of pancreas and colon cancers. This is an extremely high rate. Another striking figure is about the fact that 20% of deaths due to colon cancers arises out of hepatic metastases. In this respect, both primary cancers and metastatic cancers are of remarkable clinical significance.How is treatment applied?Micros-sphere method is based on principle of using micro-spheres that measure 20 to 50 microns in size and are labeled with Yttrium-90 – a radioactive material that emits beta particles. Micro-spheres labeled with Yytrium-90 are directly injected to arteries that supply blood directly to liver. Thus, preparation accumulates only on tumor tissues located in the liver.Since they accumulate in tumor tissues and occlude capillaries that feed tumor tissues, it is also referred as “radio-embolization method”. Femoral artery is punctured and a catheter is inserted (similar to coronary angiography), and thus, drug is directly administered into feeding artery of liver.
What are treatment methods?
There are various treatment methods for liver cancers. The first one is surgical treatment, although not all patients are eligible for surgery. This indication is related with tumor content of liver. If tumor load is very high in liver or if there is more than one lesion, surgical treatment is contraindicated. Chemotherapy and specific drugs are therapeutic options for group of inoperable patients. However, primary cancers of liver are particularly resistant to therapy.Since metastatic lesions are usually multiple in nature, strong response to therapy methods mentioned above cannot be obtained. Therefore, radioembolization method is used that is recently introduced to clinical use. In radioembolization method, microspheres (20 to 50 microns in size) labeled with radioactive material are directly delivered to feeding artery of liver and thus, therapy is applied.What are advantages and disadvantages of the method?Being a local therapy and absence of exhaustive side effects that are observed in chemotherapy are most significant advantages of micro-sphere method. The second advantage is that this therapy method can be easily applied to patients who already received chemotherapy, chemoembolization therapy or surgical treatment. Briefly, micro-sphere method can be combined with other treatments. If therapy helps findings of cancer, the procedure can be repeated, if required.Which patients are eligible for micro-sphere method?Since this method primarily targets liver cancers, they are applied to both metastatic or hepatocellular cancers. However, this therapy is not a therapeutic option in this combined group of patient, if tumor load is high, or in other words, liver is largely infiltrated. If patient has a condition of liver failure, it will be useless again. Preliminary tests are analyzed to determine patients who are eligible for this method.How many patient received this therapy and what is success rate?To date, many patients received this therapy worldwide. This procedure has been widely used in Turkey approximately for 4 to 5 years. This specific method is applied in several healthcare facilities in our country. Approximately 200 patients received this therapy per annum. This implies that minimum 1000 patients are treated, to date, with this method in Turkey, but it has been very widely used in U.S. and European countries for 10 to 15 years.Neuro-endocrine tumors are rich in somatostatin receptors (SSTr).Group of tumors rich in SSTrGastroenteropancreatic tumors (carcinoid, gastrinoma, insulinoma, glucagonoma, VIPoma)Sympatho-adrenal system tumors (pheochromocytoma, paraganglioma, neuroblastoma, ganglioneuroma)Medullar thyroid carcinomaPituitary adenomaMerkel cell carcinomaSmall cell lung cancerBreast carcinomaMelanomaLymphomaProstate cancerNon-small cell lung cancerSarcomaRenal cell carcinomaDifferentiated thyroid carcinomaAstrocytomaMeningioma.GA68 DOTA PEPTIDE PET/CT SCAN IN NEUROENDOCRINE TUMORS (SOMATOSTATIN RECEPTOR IMAGING)Conventional imaging methods are characterized with very limited performance and low sensitivity in staging, re-staging and evaluating therapy response in neuroendocrine tumors. Since glucose metabolism is slow in neuroendocrine tumors, sensitivity of FDG PET/CT scan is low. Since SSTr is imaged with GA 68 DOTA Peptide PET/CT scan, molecular SSTr content of neuroendocrine tumor is demonstrated in high sensitivity with this method.INDICATIONS OF GA 68 DOTA PEPTIDE PET/CTInvestigating localization and metastatic focus of primary tumor (staging)
Determining presence of residue, recurrence or progression (re-staging)Determining indication of Lu-177 therapy in case of metastatic disease according to Ga68 peptide uptake.Response to therapy (surgery, radiotherapy, chemotherapy or Lu-177 Peptide therapy)Special precautions taken before or after imaging. This examination is absolutely contraindicated only for pregnant women. GA 68 DOTA Peptide PET/CT imaging is similar to FDG PET/CT scan in terms of imaging technique. The only difference is radiopharmaceutical agent used.
Lutetium (Lu-177) PEPTIDE THERAPY IN NEURO-ENDOCRINE TUMORSSince Lu177 is a radionuclide that emits beta particles, it penetrates into tissue by 1 to 3 mm. Based on this characteristic, it enables specific and internal radiotherapy approach. Positive lesions on Ga 68 DOTA Peptide PET/CT will point out uptake of Lu177-labelled peptide.Lu-177 peptide is indicated for management of all inoperable and/or metastatic neuroendocrine tumors that show positive SSTr content on Ca 68 DOTA Peptide PET/CT scan.Administration: Lu177-labelled peptide is diluted with isotonic sodium chloride (10-100 ml) and intravenously infused at 10 to 20 minutes. Patient should stay, minimum for one day, in a single room that is specifically licensed by Turkish Atomic Energy Authority regarding radiation safety. Therapy cycle periods: Lu therapy is usually given in 4 to 5 cycles at 6- to 8-week intervals.
What are side effects?
Acute side effects: Nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain.Nephrotoxicity: Nephrotoxicity is minimized, to the possible extent, with renoprotective therapies.Bone marrow toxicity: It is a reversible condition that develops in 2-5% of patients especially if patients have diffuse bone metastasis.Efficiency of TreatmentLu177 have been used worldwide in management of neuroendocrine tumors approximately for one decade. This therapy has been available in particular healthcare facilities in our country approximately for 3 years. Literature data demonstrated that Lu-177 peptide prolongs survival, improves symptoms, restores biochemical markers into normal range and contributes to enhancement of quality of life in patients with SSTr-positive neuroendocrine tumor.
GALLIUM (68Ga)-LABELED PSMA PET IN PROSTATE CANCER
Prostate cancer is the second most common type of cancer in male subjects and sixth most common disease among all causes of death. Similar to all other cancer, it is very important to determine best therapy method timely in prostate cancers.Recently, total body is scanned and metastatic status of prostate cancer can be determined with Gallium (68Ga)-labeled PSMA PET scan. PSMA is a substance that is totally specific to prostate gland. When this substance is used in Galium (68Ga) PET scan, uptake is observed only in regions which are involved by prostate cancer.Current status of disease is revealed out with Galium(68Ga)-labeled PSMA PET scan and thus, best therapy method is selected.

Yusuf Demir
M.D.

Medical Oncology
The Medical Oncology Department deals with Adult Oncology cases including Lung, Breast, Prostate, Gastrointestinal (Intestinal, Pancreatic, Stomach etc.), Thyroid, and Gynecological cancers. The entire spectrum of neoplastic diseases including benign and malignant cancers are treated at our Oncology Center. A multidisciplinary approach is used during the diagnostic and treatment stages to provide the best possible treatment in a patient specific approach. The latest Chemotherapy, Immunotherapy and Targeted Smart therapy protocols are some of the treatment modalities used at our clinic.
Oncology deals not only with diagnosis and treatment of all tumors and also all developments in this field. Many studies are conducted and new techniques are developed to ensure early diagnosis of various types of cancers. Computed tomography, ultrasound, nuclear magnetic resonance imaging and PET/CT are only some examples.
Chemotherapy uses potent medicines to destruct cancerous cells. The drugs are usually injected or administered by drop counter. This therapy may, sometimes, require staying at hospital.
Chemotherapy is accompanied by side effect, because drugs may also damage healthy cells. Hair loss, tiredness, feeling sick, vomiting and immunodeficiency can be observed. Sexual life of people can be also influenced. Patients may generate various reactions; all these reactions do not always develop simultaneously.
Treatment and follow-up are planned and applied for patients, who are diagnosed with cancer, at Department of Medical Oncology in our hospital. Relevant Surgeons and Radiation Oncologists cooperated in treatment and follow-up of these patients, if required. Advancements in treatment plans ensure that patients are followed up by Medical Oncologist, Chemotherapy Nurse, Radiologist, primary surgeon, a psychologist experienced in oncology and Dietetics and Nutrition Expert and treatment is personalized according to needs of patient. Our principle in treatment of patient is to play efficient role in resolving medical conditions, including but not limited to infections, renal failure, heart failure, nutritional disorders and so on, which are secondary to chemotherapy. Chemotherapy agents, which are intravenously infused, are prepared safely by an expert Chemotherapy Nurse in a special environment. At this outpatient clinic, patients are referred to inpatient settings for chemotherapy administrations, if required.
Diagnosis and treatment services are available for types of cancers written below at Department of Medical Oncology:
• Lung cancer
• Prostate Cancer
• Breast cancer
• Head & Neck cancer
• Stomach – bowel cancers
• Brain Tumors
• Pancreatic Cancer
• Liver cancers
• Gall bladder and biliary tract cancers
• Malignant mesenchymal tumors
• Kidney and urinary bladder cancers
• Melanomas and lymphomas
• Thyroid cancer
• Testicular Cancer
• Ovarian, endometrial and cervical cancers

Abdallah TM SHBAIR
M.D.

Assoc. Prof. Dr.
Serap KAYA
Interventional Radiology
The Interventional Radiology department led by Prof. Dr Ahmet Kemal Fırat is high experienced in endovascular treatment modalities which are often required for certain neoplasms. These treatment options include endovascular embolization, deep tissue biopsies, chemotherapy catheter placement procedures and TARE/ TACE procedures. Our Cancer Center is able to offer patients minimally invasive procedures to increase patient comfort and enable complex cancer treatment options.
Our interventional radiology center, which is the therapeutic department of radiology, helps other clinical branches in many issues by applying the necessary treatment protocol with imaging devices such as angiography, computed tomography, ultrasonography, and magnetic resonance by using special needles, wires and catheters without creating a surgical incision.Interventional procedures that do not require surgery are performed under local and sedation anesthesia, making sure that the patient is comfortable, and drugs that relaxes the patient are given intravenously. This way, patients can be treated comfortably without feeling any pain. For these processes, the materials are specially designed and produced for each process and purpose, using mostly high-tech devices. These methods, which are painless and have very low risks, increase the quality of life of the patients, shorten the hospital stay, and patients are discharged on the day of the procedure or usually one day later.Special operations performed at our centerIn interventional radiology, biopsies can be taken from many organs such as liver, breast, lymph nodes, prostate; cysts and abscesses can be treated; clogged bile and urinary tracts can be opened; dialysis catheters can be inserted, and especially liver tumors can be treated by burning with special needles and drugs. Bubbles that cause brain hemorrhage or vascular diseases that cause stroke are also treated interventionally without opening the skull.Main operations performed in our center
- Tumor Marking
- Drainage (Liquid Discharge) Operations: Kidney and Urinary Tract Interventions, Abscess Drainage
- Biopsies
- Intravenous Catheters: Dialysis Catheter Insertion, Port Insertion,
- Picc-Line Catheter Installation
- Vascular Treatments: Vascular Occlusion Treatment,
- Diabetic Foot treatment
- Intracranial Vascular Aneurysm Treatment
- Bubbles that cause bleeding in the vessels feeding the brain can be treated by entering the vein. By using metallic stents and coils, the bubbles are occluded and bleeding is prevented.
- AVM Embolization

Prof.
Ahmet Kemal FIRAT
M.D.

Radiation Oncology
The Radiation Oncology Department works in close conjunction with the Medical Oncology Department to provide radiotherapy treatment modalities for cancer patients. IMRT, VBRT, brachytherapy and the entire spectrum of radiotherapy protocols are available at our clinic. The latest technology is employed to provide comprehensive treatment options to our patients.
RADIOTHERAPY
Radiotherapy; radiotherapy is a treatment modality that applies radiation to the location of tumor in order to destruct it or sometimes to eliminate adverse events caused by the tumor. Therefore, it is colloquially referred as “radiation therapy” or “X-ray therapy”. X-ray beams are used to prevent growth of cancerous cells or to kill them at the locus of treatment. Radiotherapy is a commonly used treatment modality of cancer. In fact, radiotherapy may be required at least once in 60-80 percent of cancer patients, after diagnosis is made.How is the treatment method selected?There are many factors that influence selection of treatment method. Most important ones are patient’s age, general health status, type of cancer, extent of metastasis and localization. Treatment-related decisions are made with multidisciplinary approach, a process that requires examination of the patient by many specialists from multiple relevant medical departments. A unique diagnostic and therapeutic plan is made and employed for each patient. Even if patients have same type of cancer, treatment should be planned according to conditions specific to the patient.Who is included in the therapy team?Radiation Oncologist They are responsible for determining dose of therapy delivered to which body region and how therapy will be modified according to response to radiotherapy and for evaluating side effects experience by physician.Radiation physicist: This person is responsible for planning therapy and coordinating quality, safety and technical service and maintenance of devices. She/he works together with radiation oncologist in therapy planning and application.Radiotherapy technicians: These people are trained to use radiotherapy devices. They do not stay with the patient in the same room during therapy; however, they are continuously in communication with the patient through a monitor found in the control room. They are responsible for positioning the patient correctly, operating the device and taking evaluation x-ray films during therapy.Oncology nurse: S/he is a member of the team who stays most close to the patient, along with radiation oncologist, during treatment and follow-up of the patient. They act like a bridge between the physician and the patient to manage issues such as side effects and “Do’s and Don’ts”.
How is radiotherapy applied?
Radiotherapy is a matter of teamwork and requires a process. The patient needs to have a tomography scan for radiotherapy planning. While tomography is scanned, the patient is placed on a flat table and scanning is performed in a comfortable position, provided that the target area is included. On tomography scan, target organ and adjacent organs are identified in every slice in digital media. An accurate plan is made for each patient after radiotherapy dose, exposure of intact organs to how much dose and potential risks are calculated. Next, in the first day of radiotherapy, the patient is placed on the table at exactly the same position and radiotherapy plan is applied on the patient. At this stage, conformity of therapy plan is accurately verified on the patient in the digital media and each session is completed. Radiotherapy is applied for five days in weekdays and the therapy is skipped in weekends. It takes 10 to 15 minutes to verify therapy fields and 3 to 5 minutes to delivery radiation beams. Similar to roentgen scan, patient feels no pain while radiotherapy is applied; moreover, patient is monitored by technicians with camera at different angles.RADIOTHERAPY DEVICE IN OUR HOSPITAL AND ITS SPECIFICATIONSLinear Accelerator (LINAC) TRILOGY device, that includes 5 radiotherapy methods including CONFORMAL, IMRT, VMAT, SRS and IGRT, is used for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes.3D CONFORMAL3D CONFORMAL radiotherapy implies a therapy planning procedure where 3D tumor volume and critical organs are drawn using computed tomography images. In this modality, it is aimed to give the normal tissue the lowest possible dose while obtaining a dose that surrounds the tumor in a best possible way by giving a certain margin of target volume by multi-leaf collimators (Multi-leaf Collimator-MLC) of the linear accelerator.IMRTWith IMRT, intensity of X-ray beam is modulated. Thus, the intensity of the radiation in therapy area is adjusted and dose distribution is almost optimized. While high doses are applied to tumor, healthy tissues are conserved to the maximum extent.VMATVMAT (Volumetric Intensity Modulated Arc Therapy); it is a method of radiotherapy in which therapy is given in a very short period of time. In VMAT, duration of therapy is short relative to devices that do the same job. When radiation time of 2-3 minutes is added to imaging time that is less than 2 minutes, daily therapy is completed in 4 minutes totally in VMAT. While VMAT is performed, MLCs are moved according to positions of tumor and critical organs, and gantry and dose speeds are also changed during irradiation. Higher dose is more precisely targeted to the tumor using one or more than one arcs around the patient, while protection of sensitive organs is further maximized. With these features, VMAT can be defined as a simple, fast and effective radiotherapy method that hits the target precisely and correctly.
SRSCRS SRS technology enables punctuate radiation. With this method, punctuate radiation can be given to very small tumors that measure several millimeters in size. Therefore, while the tumor is applied high radiation dose, surrounding normal tissue is given lower amount of radiation.IGRTImage guided radiotherapy can be applied with IGRT. Image Guided Radio Therapy (IGRT) can be performed by using X-ray source on the remote control handles that are installed on the main body of our device, and reciprocal detector. With the help of IGRT feature, kV-kV image of the area of the patient, that will be treated, and Digitally Reconstructed Radiotherapy (DRR) images, those are taken by planning computer, can be evaluated in 2 dimensions before each therapy, and more importantly, Computed Tomography images can be obtained by turning robotic arms of the therapy device around the patients, and these images can be compared to reference images those are obtained by CT, that was scanned previously at simulation phase. Therefore, the patient can be included in therapy with same repeatability every day, and “set-up” uncertainties, those are originating from movements of organs, are minimized.

Elnur SAHIBOV
M.D.

Pathology and Genetics
Biopsy results are generally regarded as the golden standard of diagnosis. Our hospital is equipped with a dedicated pathology lab capable of frozen section studies along with conventional and advanced pathological studies including immunohistochemical staining, immunofluorescence approaches and advanced genetic studies. Pathology Biopsy results form the basis of diagnosis and advanced genetic and hormone testing allow for patient-specific treatment approaches a such as immunotherapy and targeted smart therapy protocols.
Pathology literally means the science of disease. It examines the changes that occur at the cellular level in organs as a result of diseases. Tissue and cell samples are examined, and when necessary, they are examined by using techniques such as histo (cyto) chemistry, immune histo (cyto) chemistry, immunofluorescence, and FISH, in addition to the usual methods. Pathology diagnoses diseases by the appearance of cells under the microscope.In a pathology laboratory, cervicovaginal smear, fine-needle aspirations, tru-cut biopsies, small biopsies, excisional biopsies and operation materials are performed in detail, and if necessary, accompanied by USG or CT. In the cervicovaginal smear examination, liquid-based smear technique is used.In the examination of biopsy and operation materials, especially in tumor cases, it is recommended to perform advanced staining studies, such as histochemical and immune histochemical studies, if necessary.Emsey Hospital Pathology unit is in contact with all branches because of the multidisciplinary working principles of our hospital.

Prof.
Hayreddin YEKELER
M.D.
sasaas